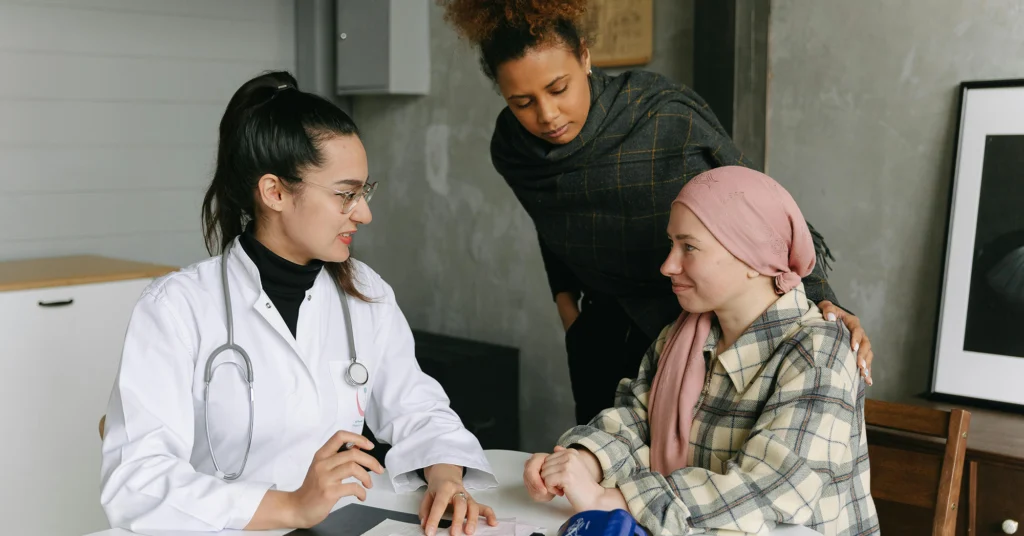
When it comes to gynecologic cancer, your knowledge is power. At WMCHealth, we can help you know your risks and recognize warning signs to help detect cancer early when it’s easiest to treat. Early treatment means the best possible chances for a healthy life after cancer. Our gynecologic oncology team can diagnose and treat any type of gynecologic cancer with the most advanced and minimally invasive technologies—all while keeping you close to home.
A cancer diagnosis can be scary. And treatment can be challenging. At WMCHealth, we know how important it is to have a compassionate care team by your side who has the expertise to provide the best possible care.

An Innovative, Multidisciplinary Approach
The Division of Gynecologic Oncology and Robotic Surgery at WMCHealth has a simple mission: to provide our patients with the most comprehensive, compassionate and personal gynecologic care. We have access to the most advanced innovations and technologies in treating gynecologic cancers and performing gynecologic surgeries. Our division partners with nationwide cancer researchers on clinical trials funded by the National Cancer Institute to better map out treatment approaches for all types of gynecologic cancers.
WMCHealth is a referral center for complex radiation treatment, including both external beam RT and brachytherapy. We provide access to recent clinical research, including clinical trials, along with collaborative care with experts in radiology, pathology, palliative care, pain services, and radiation therapy. With our expertise and access to the latest in gynecologic care, you and your loved ones are in the right hands.
What Is Gynecologic Cancer?
Gynecologic cancer is any cancer that begins in a woman’s reproductive organs in the pelvic area.
Signs and symptoms of gynecologic cancer vary from person to person. It is important to listen to your body and know what is normal for you, so you can recognize warning signs quickly.
Symptoms of Gynecologic Cancer
Each gynecologic cancer has its own set of symptoms. But common symptoms may include:
- Constipation
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Vaginal bleeding or discharge
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Itching, burning, pain, or soreness in the skin
Speak with your doctor if you experience any warning signs that last for two weeks or longer, especially if you’re experiencing symptoms that are unusual for you. While an underlying condition other than cancer may be the cause of your symptoms, your doctor is the only person who can give you a proper diagnosis. Having regular gynecological exams may also help to catch gynecologic cancer early.
Types of Gynecologic Cancer

There are five main types of gynecologic cancer. At WMCHealth, we are experts in all of these forms of cancer and can help you manage your path to care.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer begins in the cervix, which is the lower, pear-shaped area of the uterus (the womb where a fetus would grow). Human papillomavirus (HPV) can cause cervical cancer. HPV is found in more than 99% of cervical cancers and is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the U.S.
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer can begin in the ovaries, which are located on each side of the uterus. (Ovaries make female hormones and produce eggs for reproduction.) Ovarian cancer can also begin in the fallopian tubes or peritoneum (a sheet of smooth tissue that surrounds your abdominal organs).
Uterine Cancer
Uterine cancer (endometrial cancer) begins in the lining of the uterus. Factors that can increase your chances of developing uterine cancer include being overweight or over the age of 50.
Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer begins in the vagina, which is also known as the birth canal. This type of gynecologic cancer is very rare, accounting for less than 7% of all gynecologic cancers in the U.S.
Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer begins in the vulva, which is the outer part of your genital organs that has two folds of skin called the labia. Vulvar cancer usually occurs on the inner edges of the labia. This type of gynecologic cancer is also very rare, with about 100,000 diagnoses in the U.S. each year.
Know Your Risk for Gynecologic Cancer
Being aware of your risk factors for any health condition can help you take steps to be prepared and proactive. There are a few important risk factors to keep in mind. These include:
- Family history and genetics: Mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes can increase your risk of ovarian cancer. If your mother, daughter, or sister has breast cancer or gynecologic cancer, you may have an increased risk for developing these cancers.
- Obesity: Obesity can elevate estrogen production and trigger chronic inflammation, potentially impacting the endometrial lining of the uterus and heightening the risk of developing this type of cancer.
- Age: Most gynecologic cancers are diagnosed in women over the age of 50.
- HPV: HPV is a sexually transmitted disease strongly tied to gynecologic cancer. HPV causes nearly all cases of cervical cancer. Many strains of HPV can cause vaginal and vulvar cancers.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of certain types of gynecologic cancers, such as cervical cancer.
- High blood pressure: Women with high blood pressure may have an increased risk of developing ovarian cancer and uterine cancer.
Diagnosing Gynecologic Cancer
To diagnose gynecologic cancers, your doctor will first review your medical history, ask about symptoms you have, and determine whether you have any risk factors. Your doctor will then perform a physical exam, including a pelvic exam.
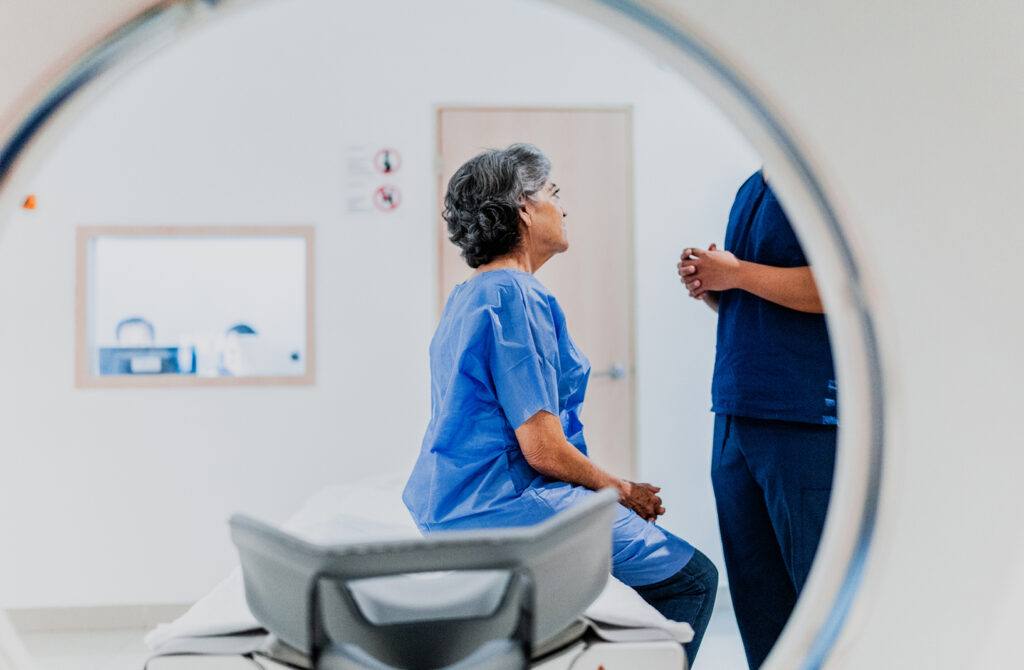
If your doctor suspects you have gynecologic cancer, they will order diagnostic tests to confirm. These may include:
- Pap smear
- Blood tests
- Imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT
A biopsy is always needed to confirm a gynecologic cancer diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small piece of tissue is removed and collected. A pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to detect the presence of cancer cells.
Treatments for Gynecologic Cancers
Gynecologic cancer treatment widely varies depending on the type of cancer and whether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Treatment may include one or more options to prevent continued growth or a spread into other parts of the body:
- Surgery, including minimally invasive robotic surgery, to remove cancer tissue
- Radiation therapy to kill cancer cells
- Chemotherapy to shrink or kill cancer cells
At WMCHealth, cancer treatment goes beyond treating you physically. We know the cancer journey is emotionally and mentally challenging. We offer extensive resources in the form of support groups, palliative care, survivorship programs, and social services.
Where Innovation Meets Compassion
Our gynecologic oncologists create a compassionate connection with patients to treat even the most complex gynecologic conditions.